Baigong Pipes Mystery: The Iron Pipes Buried in China’s Mountains
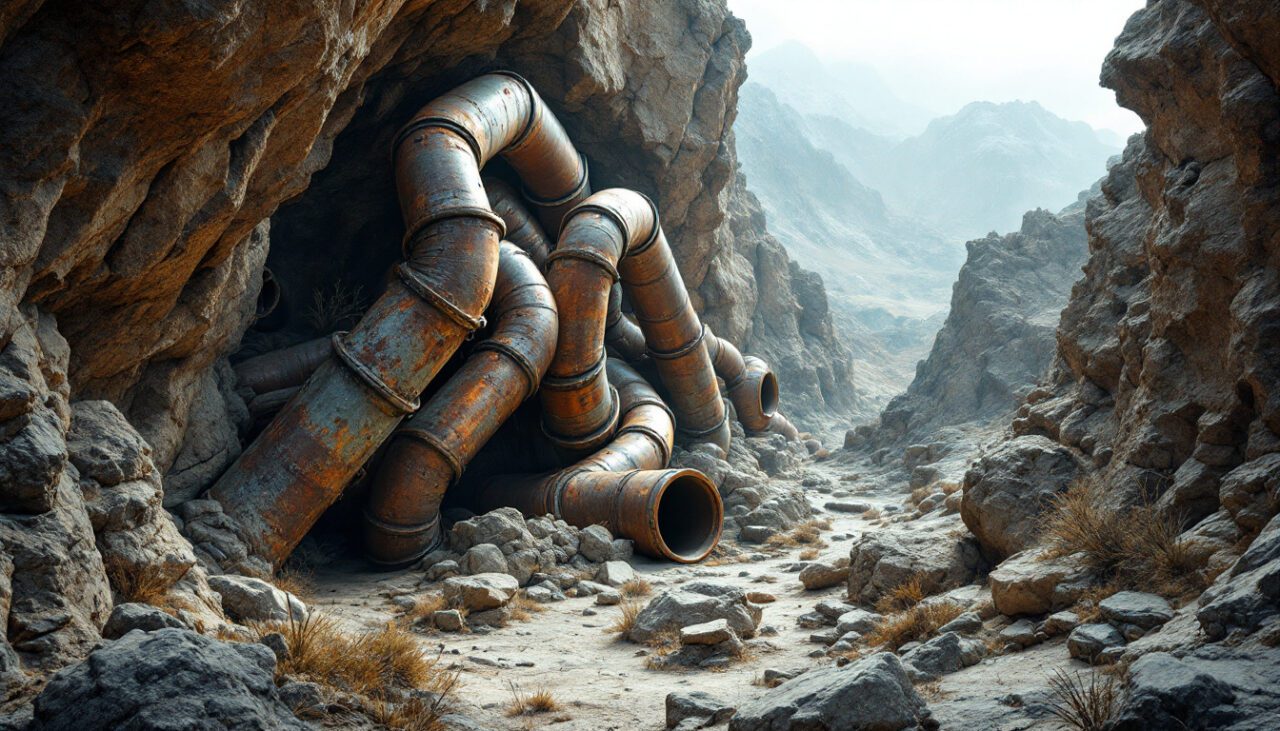

The enigma of the Baigong Pipes challenges conventional archaeological understanding.
Embedded within China’s remote Qinghai Province, these metallic tubes, fused with ancient rock and radiating from Mount Baigong’s slopes, defy simple explanation.
Scientists debate their 150,000-year-old origins—natural geological formations, petrified tree roots, or perhaps something more provocative.
Recent government restrictions on the site have only deepened the mystery, leaving unanswered questions about what these rusted cylinders might reveal about Earth’s technological past.
Summary & Key Takeaways
Hide- The Baigong Pipes are a network of metallic tubes discovered in 1996 in Mount Baigong, China, sparking archaeological intrigue.
- Pipes vary from microscopic to 40cm in diameter, containing 30-40% iron oxide and estimated to be 150,000 years old.
- Multiple theories exist, including natural geological formation, fossilized tree roots, ancient engineering, and extraterrestrial origin.
- The Chinese government has imposed strict access restrictions since the early 2000s, limiting scientific investigation of the site.
- Discovered within a three-chambered cave system at 2,800m elevation, some pipes are precisely aligned and embedded in solid rock formations.
Discovery of the Pipes in China’s Remote Mountains

The discovery of the enigmatic Baigong pipes in 1996 stunned researchers who ventured into China’s remote Qinghai Province, where Mount Baigong rises dramatically from an otherwise barren landscape near Toson Lake.
Initial reports from Chinese scientists described an intricate network of metallic tubes, some as large as 40 centimeters in diameter, protruding from cave walls and extending into the nearby saltwater lake, prompting immediate speculation about their seemingly impossible origin.
The mystery deepened when local Tibetan nomads shared centuries-old legends about “iron pipes placed by celestial beings,” adding a cultural dimension to what would become one of archaeology’s most perplexing puzzles.
Much like the quest for El Dorado’s legacy, the Baigong pipes continue to generate debates about the relationship between archaeological fact and cultural folklore.
The Location: Mount Baigong and the Surrounding Landscape
The enigmatic Baigong Pipes emerge from a three-chambered cave system nestled in Mount Baigong, approximately 40 kilometers southwest of Delingha city in China’s remote Qinghai Province.
This harsh, desolate region lies at an elevation of 2,800 meters above sea level, characterized by its rust-colored soil, sparse vegetation, and the nearby salt-encrusted shores of Lake Toson, a body of water with unusually high saline content.
The extreme isolation and inhospitable nature of the landscape—subjected to dramatic temperature fluctuations, limited rainfall, and thin mountain air—intensifies the archaeological mystery, as the technological sophistication necessary to install such pipe structures seems incongruous with the site’s challenging environmental conditions.
The complex pipe formations share similarities with the diplomatic correspondences discovered at Hattusa, in the way they challenge our understanding of ancient technological capabilities.
Description of the cave system near Delingha
Nestled within the rugged terrain of China’s Qinghai Province, a mysterious cave system near Delingha has become the focal point of scientific intrigue and speculative wonder.
The network comprises three caves with unique geological formations, their walls embedded with mineral deposits that chronicle millennia of natural history.
While compelling for spelunking adventures, the caves’ true ecological significance lies in their unexplained metal pipes.
Much like debates surrounding the Richat Structure and its possible connection to Atlantis, these caves prompt scientific investigation using remote sensing and archaeological methods.
Environmental conditions and terrain characteristics
Standing in stark contrast to China’s densely populated eastern seaboard, Mount Baigong rises from the Qaidam Basin at an elevation of 2,000 meters above sea level, in a region characterized by extreme temperature fluctuations and sparse precipitation.
The terrain analysis reveals:
- Ancient lakebed sediments suggesting geological history spanning millions of years
- Climate variations producing freeze-thaw cycles that greatly impact rock formations
- Limited biodiversity assessment due to harsh conditions
- Ecological impact of sustained drought periods
Similar to the remote sensing technologies that helped archaeologists detect potential remnants of Iram beneath the sands, modern geological surveys have provided crucial insights into Mount Baigong’s formation.
Early Reports and the Start of the Mystery
The Baigong Pipes first entered public awareness in 1996 when the state-run Xinhua News Agency published reports of strange metallic conduits embedded in a remote mountainside, prompting immediate curiosity from both local villagers and scientific researchers.
Ancient legends from the region had long referenced mysterious “sky people” who reportedly descended to Earth with metal objects, stories that suddenly gained renewed significance as investigators documented the extensive network of pipe-like structures.
Chinese scientists, initially skeptical yet intrigued, began formal investigations into the site, marking the beginning of an archaeological enigma that would challenge conventional understandings of the region’s technological history.
The excavation techniques employed at Baigong shared methodological similarities with those used to uncover Phoenician artifacts throughout the Mediterranean, demonstrating how archaeological practices transcend cultural boundaries.
Initial documentation and Chinese press coverage
Several Chinese newspapers first reported the enigmatic Baigong Pipes in 1996, when a group of scientists dispatched to investigate caves near Mount Baigong in China’s Qinghai Province encountered what appeared to be manufactured metal tubes embedded in the rock face.
Initial documentation highlighted:
- Unexpected media portrayal generating international curiosity
- Scientific skepticism regarding their authenticity
- Significant investigative challenges due to remote location
- Cultural implications for understanding advanced ancient technologies
The absence of definitive explanations for the Baigong Pipes mirrors the enduring mystery of the Mary Celeste, where despite multiple official inquiries conducted, investigators produced more questions than conclusive answers about their origin.
Role of local legends and interest from researchers
Long before international media caught wind of the Baigong Pipes phenomenon, indigenous Tibetan and Mongolian populations living near Mount Baigong had woven tales of mysterious metal structures into their cultural narratives.
These regional myths gained scientific curiosity in the late 1990s when research collaboration began examining the pipes’ cultural significance.
Local folklore preserved oral histories of the structures, which scholars now consider invaluable contextual evidence alongside geological studies.
Similar to the enigmatic Croatoan carving left behind at Roanoke Colony, these ancient tales provide tantalizing clues that continue to challenge conventional historical narratives.
Material Analysis and Scientific Observations
Laboratory analysis of the Baigong pipes has revealed a perplexing mixture of organic and inorganic materials, including iron oxides, silicon dioxide, and rare earth elements that challenge conventional explanations about their origin.
The pipes exhibit unusual metallurgical properties, with scanning electron microscopy showing microstructures inconsistent with both primitive human manufacturing techniques and natural geological formations.
These anomalous characteristics have prompted scientific debate regarding whether they represent an advanced prehistoric technology, unusual but natural geological phenomena, or perhaps evidence of materials altered through centuries of exposure to the region’s unique mineral-rich environment.
Similar to the Antikythera Mechanism, these findings have sparked debates about ancient technological capabilities and how they challenge our understanding of historical technological advancement.
Physical Characteristics of the Pipe Structures
The enigmatic Baigong pipes, discovered protruding from the sandstone slopes of Mount Baigong, exhibit remarkable diversity in their dimensions, ranging from microscopic tubes merely millimeters in diameter to substantial conduits approaching 40 centimeters across.
Many of these cylindrical structures appear permanently fused with the surrounding rock formations, presenting a perplexing integration that has confounded conventional archaeological explanations.
Their surfaces display extensive weathering patterns and a distinctive rust-colored patina, properties which have prompted scientific debate regarding their true composition and, more provocatively, their actual age.
Similar to Göbekli Tepe, the Baigong pipes challenge established timelines and may require a complete reevaluation of humanity’s technological capabilities in prehistoric times.
Varying sizes, some embedded in rock
Physical examination of the Baigong Pipes reveals an intriguing variety of dimensions, with diameters ranging from microscopic capillaries measuring just a few millimeters across to substantial conduits exceeding thirty centimeters in width.
Their geological embedding offers clues to potential origins:
- Horizontal pipes display consistent rust characteristics
- Vertical conduits follow precise pipe alignment
- Embedded specimens penetrate solid rock formations
- Surface pipes exhibit varied dimensions and weathering patterns
Similar to how strategic advantages positioned Carthage as a Mediterranean power, the Baigong Pipes’ positioning within the mountain suggests purposeful placement rather than random formation.
Surface weathering and rusted appearance
Surface examination of the Baigong Pipes reveals extensive weathering patterns and pronounced oxidation, suggesting prolonged exposure to environmental elements.
Scientific surface analysis documents advanced corrosion effects, with rust formation permeating even deeply embedded sections.
These weathering processes, including mineral displacement and structural degradation, provide essential geological implications regarding both the pipes’ composition and their mysterious temporal placement within China’s mountainous landscape.
Lab Tests and Composition Studies
Laboratory analyses of the controversial Baigong pipes have revealed a composition primarily consisting of iron oxide (30-40%), silicon dioxide (40-50%), and calcium (6-8%), suggesting they might be naturally formed iron-rich sediments rather than artificial structures.
Chinese scientists have estimated the age of these pipe-like formations at approximately 150,000 years, predating any known human civilization capable of such metallurgical achievements and lending weight to their potential natural origin.
The high iron content, combined with evidence of possible fossilization processes, has led some researchers to hypothesize that the pipes may represent the mineralized remains of tree roots or ancient organisms that underwent replacement by iron-rich minerals through geological processes spanning millennia.
Findings on iron oxide, silicon dioxide, and calcium
Extensive chemical analysis of the mysterious Baigong Pipes has revealed a compelling mineral composition that challenges both natural and artificial origin theories.
Iron mineralogy analysis points to a delicate balance between geological significance debates and historical context exploration.
The findings show:
- 30% iron oxide, indicating extensive oxidation
- 40% silicon dioxide, suggesting geological formation
- 8% calcium deposits throughout the structure
- Trace elements matching surrounding mountain composition
Reported age estimates and possible fossilization
Scientific efforts to date the enigmatic Baigong Pipes have yielded astonishing estimates that further complicate their origin story. Various dating techniques place them between 30,000 and 150,000 years old—eons before recorded Chinese civilization.
The pipes’ integration with the rock matrix suggests possible fossilization processes, while chemical analysis reveals evidence of mineral replacement and structural transformation, challenging researchers’ understanding of their historical context.
Mainstream Theories Explaining the Pipes
Scientific investigation into the enigmatic Baigong Pipes has yielded two prevailing theories that dominate geological and archaeological discourse.
The first explanation suggests these tubular structures formed naturally through complex geological processes, perhaps involving sedimentary deposition around plant roots or iron-rich fluid crystallization in cavities.
Alternatively, some researchers propose these pipes represent sophisticated engineering by an ancient civilization, potentially employing metallurgical techniques far more advanced than previously attributed to cultures inhabiting this remote region of China.
Geological Formation through Natural Processes
Mainstream geological explanations for the enigmatic Baigong Pipes suggest they formed through completely natural processes, with ferrous oxidization creating tubular structures as iron-rich solutions permeated the surrounding sediment.
Scientists have also proposed that ancient tree roots may have fossilized in unique conditions, leaving behind hollow cylindrical spaces that later filled with iron-rich minerals, solidifying into the pipe-like formations that so perplex visitors today.
These naturally occurring geological phenomena, while seemingly improbable in their uniformity and arrangement, represent well-documented processes that have created similar formations at other sites around the world, challenging the need for more exotic explanations.
Possibility of ferrous oxidation or natural concretion
While examining the chemical composition of the Baigong Pipes, researchers have proposed that rather than being artifacts of ancient technology, these curious formations may be the result of ferrous oxidation or natural concretion processes common in specific geological environments.
The evidence supporting natural geological processes includes:
- Iron-rich mineral deposits crystallizing within sedimentary layers
- Ferrous oxidation creating tube-like structures through chemical weathering
- Similar pipe formations documented in other regions with comparable mineral composition
- Microscopic analysis revealing organic material consistent with natural concretions
Hypotheses involving root fossilization
Root fossilization, a compelling alternative explanation for the Baigong Pipes, positions these enigmatic formations as the mineralized remains of ancient tree roots that once penetrated the mountain’s geological strata.
Geological processes transformed these root structures through mineralization, preserving their intricate networks within the rock.
The fossil distribution patterns mirror ancient ecosystems rather than artificial constructions, potentially revealing evolutionary significance of prehistoric flora that once thrived in this now-barren landscape.
Human-Made Origins from Ancient Civil Engineering
Some archaeologists propose that the Baigong Pipes represent an ancient engineering feat, possibly evidence of early metallurgical knowledge or a sophisticated drainage system developed by a previously unknown civilization.
This theory, though compelling in its recognition of the pipes’ seemingly deliberate arrangement and uniform composition, faces significant challenges when confronted with the conspicuous absence of associated settlements, tools, or cultural artifacts in the surrounding region.
The stark isolation of these structures within the barren landscape raises profound questions about who might have created them and why they would establish such an elaborate system in such a remote location.
Suggestions of early smelting or drainage technology
According to several archaeometallurgists investigating the Baigong Pipes, these unusual structures may represent early evidence of metalworking technology or sophisticated drainage systems implemented by ancient civilizations in the region.
Analysis reveals four significant technological implications:
- Advanced ancient metallurgy techniques predating current historical timelines
- Innovative drainage systems designed for resource management
- Potential cultural significance connecting engineering to social structures
- New archaeological techniques required for proper contextual understanding
Lack of nearby settlements or tools
One significant challenge to the human-made origin theory of the Baigong Pipes stems from the puzzling absence of archaeological evidence typically associated with ancient settlements.
Modern excavations, hampered by isolation challenges and exploration difficulties, have revealed no tools, remnants of dwellings, or evidence of contemporary technology in the vicinity.
The remote logistics of the site raise questions about how ancient peoples navigated the archaeological impact in such inaccessible terrain.
Alternative Explanations and Fringe Ideas
Beyond mainstream scientific hypotheses, several fringe theories have emerged that attribute the Baigong Pipes to extraterrestrial intervention, suggesting they might be remnants of ancient alien technology or landing infrastructure.
Some alternative researchers propose the pipes could be artifacts from a technologically advanced lost civilization that inhabited the region long before recorded history, perhaps related to legends of Lemuria or other purported prehistoric cultures.
These unconventional explanations, while lacking substantive evidence, persist in popularity due to the pipes’ unusual placement, composition, and the challenging questions they pose about humanity’s technological capabilities in deep antiquity.
Proposals Involving Extraterrestrial Influence
The Baigong Pipes‘ remote location in a geographically challenging region of Tibet, far from ancient population centers, has prompted some fringe theorists to propose extraterrestrial involvement in their creation.
Ancient astronaut enthusiasts point to the pipes’ apparent complexity and precise arrangement, suggesting that such engineering feats would have been beyond the technological capabilities of early human civilizations.
These theories, while lacking scientific consensus or archaeological evidence, persist in popular culture as part of a broader pattern of attributing unexplained ancient structures to non-human intelligence.
Arguments based on remote location and complexity
Among the more persistent arguments advanced by ancient astronaut theorists regarding the Baigong Pipes is their peculiar geographical situation, nestled in an area so remote and inhospitable that conventional wisdom struggles to explain why ancient humans would undertake such an elaborate construction project there.
Proponents highlight:
- Extreme isolation impact limiting archaeological access
- Complexity factors exceeding presumed ancient capabilities
- Remote analysis suggesting intentional design
- Geological implications of non-natural formations
Theories shared by ancient astronaut enthusiasts
While mainstream archaeology remains skeptical of otherworldly origins for the Baigong Pipes, ancient astronaut enthusiasts have developed a complex narrative of extraterrestrial hypotheses that attempt to explain these enigmatic structures.
These theories suggest the pipes represent unexplained artifacts left by advanced technology-wielding visitors, possibly connected to lost civilizations that flourished through extraterrestrial archaeology – a perspective that challenges conventional historical understanding.
Speculations on Lost Civilizations
Some fringe theorists contend the Baigong Pipes originate from an undocumented prehistoric civilization that possessed metallurgical capabilities far exceeding what mainstream archaeology acknowledges for that period.
These speculations gain traction when comparisons are drawn to other anomalous artifacts worldwide, such as the Baghdad Battery, Antikythera Mechanism, or the precisely cut stones of Puma Punku, which similarly challenge conventional historical timelines.
The shadowy suggestion of a technologically sophisticated “lost civilization” persists as an emotionally compelling explanation in the absence of definitive scientific consensus, particularly as the pipes’ uniform dimensions and apparent purposeful arrangement continue to resist straightforward natural explanation.
Discussions of unknown prehistory or advanced culture
Could the Baigong Pipes represent evidence of a sophisticated prehistoric civilization, one that possessed advanced metallurgical knowledge thousands of years before conventional history suggests? Proponents of this theory point to several intriguing possibilities:
- Lost prehistoric civilizations with advanced engineering capabilities
- Ancient technologies reflecting sophisticated metallurgical understanding
- Cultural theories suggesting knowledge transfer from unknown sources
- Lost knowledge of specialized pipe-making techniques
Parallels drawn with other unexplained artifacts
Across the archaeological landscapes of our world, the Baigong Pipes stand not in isolation but rather among a constellation of perplexing artifacts that challenge conventional historical narratives.
Similar ancient artifacts include Costa Rica’s perfectly spherical stone balls, Nazca’s geometric lines, and Baghdad’s apparent “batteries”—unexplained structures that, like the Baigong discovery, prompt historians to reconsider established timelines of human technological achievement and cultural interpretations.
Current Research and Restricted Access
Recent changes in government oversight have markedly limited outside access to the Baigong Pipes site, with Chinese authorities implementing stricter regulations that ostensibly protect the archaeological integrity of the area.
Despite these restrictions, independent researchers and fringe archaeologists continue to pursue alternative methods of investigation, including satellite imagery analysis and interviews with local witnesses who previously visited the site.
The diminishing physical access has, paradoxically, intensified interest in the pipes, transforming them from a geological curiosity into what some scholars describe as “forbidden knowledge,” thereby amplifying their mystique in both academic circles and popular imagination.
Changes in Access and Government Oversight
Access to the enigmatic Baigong Pipes has undergone significant changes in recent years, with Chinese authorities implementing increasingly restrictive visitation protocols and maintaining an ambiguous official stance regarding the site’s nature.
Foreign scientists, particularly those hoping to conduct independent analyses or collect samples, have reportedly encountered bureaucratic obstacles that prevent thorough examination of these geological anomalies.
The government’s cautious management approach has prompted speculation about their motivations, ranging from legitimate archaeological preservation concerns to more controversial theories about concealing evidence that might challenge conventional historical narratives.
Limited visitation and official stance
While the Chinese government maintained an ambiguous stance toward the Baigong Pipes for decades, official policy has greatly tightened since the early 2000s.
This transformation has turned what was once a relatively accessible archaeological curiosity into a closely monitored site with strictly regulated visitation protocols.
Current official restrictions include:
- Mandatory government guides for all visitors
- Prohibition of independent sampling or testing
- Limited research permits exclusively for approved institutions
- Designated viewing areas restricting close examination
Reported restrictions for foreign scientists
Foreign scientists have faced particularly stringent barriers when attempting to study the Baigong Pipes, creating a stark disparity between domestic and international research opportunities at the site.
Government oversight has intensified, with research restrictions implemented through international policies that limit scientific collaboration.
These transparency issues have fueled speculation about what aspects of the site Chinese authorities might be protecting or concealing from external scrutiny.
Continued Interest from Independent Researchers
Despite government restrictions, independent researchers maintain a lively online presence through speculative discussions, investigative articles, and amateur analyses that keep interest in the Baigong Pipes phenomenon alive.
The digital domain has become the primary arena where alternative theories flourish, with websites, forums, and social media channels dedicated to examining photographic evidence, historical accounts, and comparative analyses with other unexplained archaeological anomalies around the world.
These independent voices consistently advocate for greater transparency from Chinese authorities, calling for unrestricted scientific access to the site and the release of thorough geological surveys that might finally resolve whether these mysterious tubes represent ancient alien technology, natural geological formations, or something entirely different.
Online discussions and investigative articles
How extensively has the mystery of the Baigong Pipes captivated online communities across the globe? The enigma continues to generate dynamic discourse across online forums, social media platforms, and investigative blogs, occasionally reaching academic journals.
The digital conversation typically centers around:
- Geological formation theories
- Ancient civilization hypotheses
- Extraterrestrial intervention possibilities
- Scientific methodology disputes
Calls for further exploration and transparency
The quest for unrestricted scientific access to the Baigong Pipes site remains an unfulfilled ambition for researchers worldwide, who continue to advocate for thorough investigations beyond the limited studies conducted to date.
Despite growing public interest, exploration urgency faces obstacles of inadequate research funding and bureaucratic restrictions.
Many scientists argue that scientific transparency and international collaboration opportunities could finally resolve this enduring geological enigma that challenges conventional historical narratives.
Wrapping Up
As science scrutinizes the Baigong Pipes with increasingly sophisticated methods, ancient legends whisper their own explanations from the mountains’ depths.
The juxtaposition of empirical analysis against restricted access creates a paradox where answers remain tantalizingly elusive.
Perhaps the true significance of these metallic enigmas lies not in their ultimate origin, but in how they challenge our understanding of what is possible—both in nature’s processes and human history’s unwritten chapters.